The Code Default property provides an expression written in C#/Visual Basic that evaluates to an initial field value of a new data row. Database tables frequently define default column expressions that will be evaluated by the database engine when a new record is persisted. From the user perspective, it is beneficial to see what exactly will be inserted in the column at the time when the user enters the field values instead of leaving the fields blank and relying on the database to fill in the blanks. The Code Default may provide a duplicate calculation that fulfills this need.
Default Values with C# / Visual Basic
The New Orders form has two date fields, Order Date and Required Date, that should have defaults when the form is first initialized.
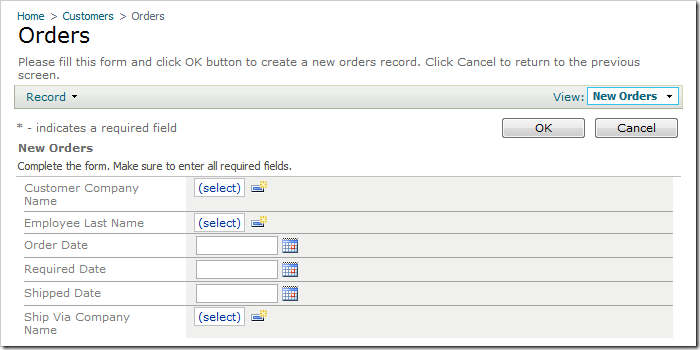
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab, and double-click on Orders / Fields / OrderDate node.
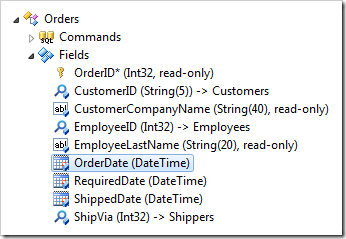
Change the Code Default:
| Property | New Value |
| Code Default | DateTime.Now |
Press OK to save. Double-click on Orders / Fields / RequiredDate node.
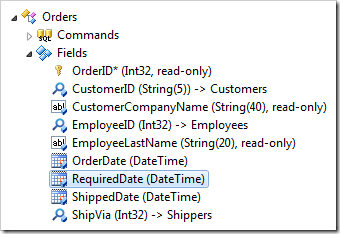
Change the Code Default:
| Property | New Value |
| Code Default | DateTime.Now.AddDays(7) |
Press OK to save. On the Project Browser toolbar, press Browse button.
Navigate to the Orders page, and create a new record. The Order Date field will be populated with the current date. The Required Date field will be populated with the date seven days in the future.
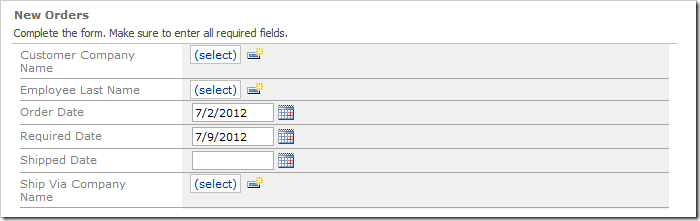
This is how the code generator incorporates the code expression in the C#/Visual Basic business rules.
C#:
using System;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class OrdersBusinessRules : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[RowBuilder("Orders", RowKind.New)]
public void BuildNewOrders()
{
UpdateFieldValue("OrderDate", DateTime.Now);
UpdateFieldValue("RequiredDate", DateTime.Now.AddDays(7));
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class OrdersBusinessRules
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<RowBuilder("Orders", RowKind.New)> _
Public Sub BuildNewOrders()
UpdateFieldValue("OrderDate", DateTime.Now)
UpdateFieldValue("RequiredDate", DateTime.Now.AddDays(7))
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
A custom utility class can be implemented for complex calculations. A static or shared property or method of the class can be used in Code Default expressions similar to how System.DateTime class is used in the example.
Default Values with SQL Business Rules
Code Default permits simple default values. For a majority of situations or when a more complex default value calculation involving interactions with the database is required, SQL Business Rules provide a great alternative.
Switch back to the Project Designer. Double-click on Orders / Fields / OrderDate field node.
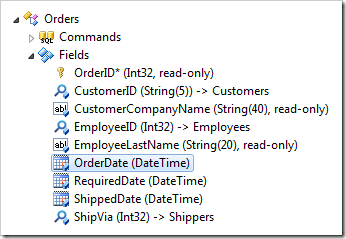
Clear the Code Default:
| Property |
New Value |
| Code Default |
N/A |
Save the field. Double-click on Orders / Fields / RequiredDate field node.
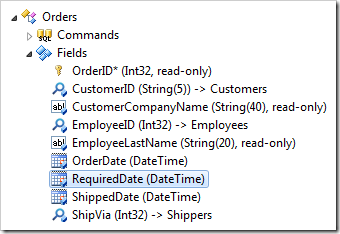
Change the following properties:
| Property |
New Value |
| Code Default |
N/A |
Press OK to save the field. Right-click on Orders / Business Rules node, and select New Business Rule option.
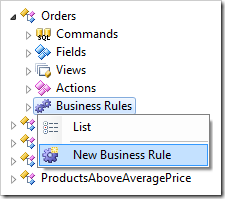
Use the following configuration:
| Property |
Value |
| Command Name |
New |
| Type |
SQL |
| Phase |
Execute |
| Script |
set @OrderDate = GETDATE()
set @RequiredDate = DATEADD("d", 7, getdate())
|
Press OK to save the business rule. On the toolbar, press Browse.
Navigate to the Orders page, and create a new order. The correct date values will be presented as default values.
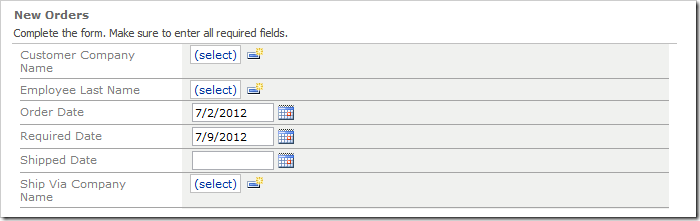
The business rule matching New command is automatically executed on the server and the values of parameters OrderDate and RequiredDate are transferred to the fields with the same name in a new row.