The CustomerID field from the Customers controller should have all values formatted in uppercase.
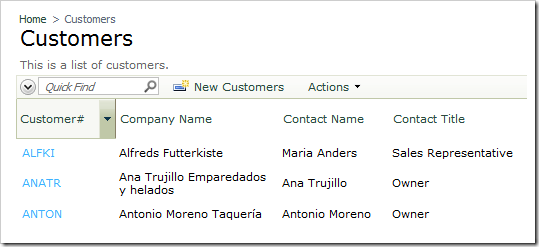
Let’s create a business rule in C# or Visual Basic to convert all user input to uppercase.
Start the Project Designer. In the Project Explorer, switch to the Controllers tab and double-click on Customers controller node.
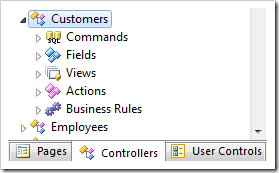
Change the Handler property:
| Property | New Value |
| Handler | CustomersRule |
Press OK to save the controller. In the Project Explorer, double-click on Customers / Fields / CustomerID field node.
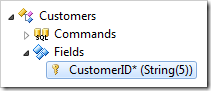
Make the following changes:
| Property | New Value |
| The value of this field is calculated by a business rule expression. | True |
| Context Fields | CustomerID |
Exit the designer and generate the application.
Click on the project name, and press Design. Visual Studio will open the project.
In the Solution Explorer, double-click on ~\App_Code\Rules\CustomersRule.cs(vb) file.
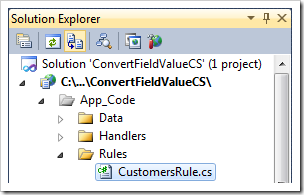
Replace the sample code base with the following:
C#:
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using MyCompany.Data;
namespace MyCompany.Rules
{
public partial class CustomersRule : MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
{
[ControllerAction("Customers", "Insert", ActionPhase.Before)]
[ControllerAction("Customers", "Update", ActionPhase.Before)]
[ControllerAction("Customers", "Calculate", ActionPhase.Execute)]
public void CalculateCustomerID(string customerID)
{
UpdateFieldValue("CustomerID", customerID.ToUpper());
}
}
}
Visual Basic:
Imports MyCompany.Data
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Linq
Namespace MyCompany.Rules
Partial Public Class CustomersRule
Inherits MyCompany.Data.BusinessRules
<ControllerAction("Customers", "Insert", ActionPhase.Before)>
<ControllerAction("Customers", "Update", ActionPhase.Before)>
<ControllerAction("Customers", "Calculate", ActionPhase.Execute)>
Public Sub CalculateCustomerID(ByVal customerID As String)
UpdateFieldValue("CustomerID", customerID.ToUpper())
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Save the file, and switch to the web application. Navigate to the Customers page, and create a new record. Type in lowercase letters for Customer# field.
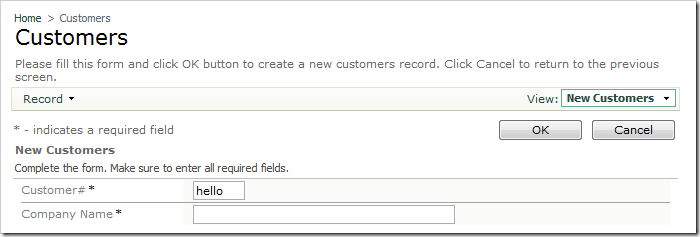
Press Tab or click on another area of the page. The text in Customer# will be converted to uppercase.
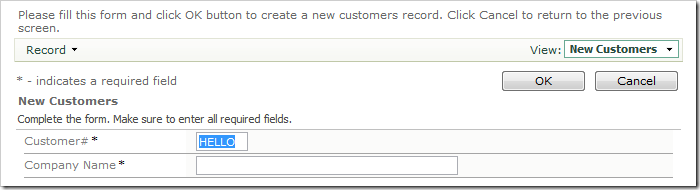
The same business logic can be implemented with the help of SQL Business Rules.